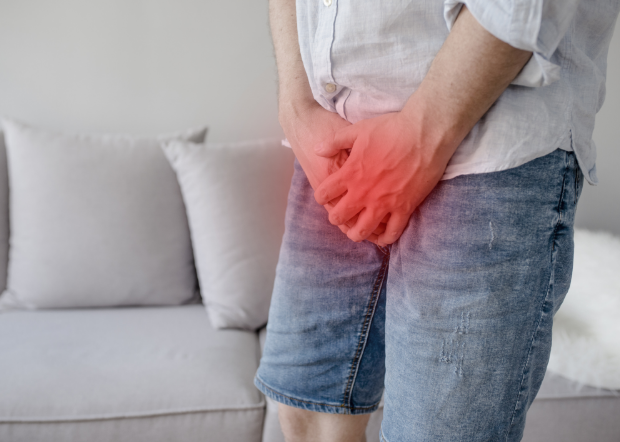
The prostate is part of a man’s reproductive system. It is located in front of the rectum and behind the bladder. Urine flows through the urethra, which is surrounded by the prostate. The prostate is a gland that secretes seminal fluid. During ejaculation, seminal fluid facilitates the removal of sperm from a man's body as part of the semen.
The prostate is approximately the size of a walnut when it is healthy. In the case of an enlarged prostate, the urethra may be squeezed. As a result, the urine flow from the bladder to the penis may be slowed or stopped.

Cancer is found only in the prostate, usually during another medical procedure. A digital rectal examination or imaging test is unable to detect it.

An imaging test cannot detect a tumour at this stage because it is too small to be felt or seen. It may also refer to a slightly larger tumour that can be detected during a Digital Rectal Examination. There is no evidence that cancer has spread beyond the prostate gland.

Cancer has spread beyond the outer layer of the prostate to nearby tissues. The disease may also spread to the seminal vesicles.

In this stage, the tumour has spread to other parts of the body, such as the bladder, rectum, bone, liver, lungs, or lymph nodes.
The exact cause of prostate cancer is unknown. In most cases, doctors cannot explain why one man develops prostate cancer while another does not. It has been shown, however, that men who possess certain risk factors are more likely than others to develop prostate cancer.
A person's age is the most significant risk factor for prostate cancer. As you age, your risk of developing prostate cancer increases. In men under the age of 45, this disease is rare.
There is a higher risk of prostate cancer if your father, brother, or son has been diagnosed with the disease.
Male Caucasians are more likely to develop prostate cancer than male Asians.
According to some studies, men who consume a diet high in animal fat or meat may be at an increased risk of prostate cancer. A diet rich in fruits and vegetables may reduce men’s prostate cancer risk.
The first indication that a man may have prostate cancer is often an abnormal finding in his routine screening test. Others may notice one or more of the following lower tract symptoms which comprise of :
It is also possible that some of these symptoms indicate a common, non-cancerous condition called Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH), which is an enlargement of the prostate gland. If you experience any of these symptoms, you should seek medical attention as soon as possible to ensure proper diagnosis and treatment.
The following clinical findings and laboratory tests can be used to diagnose prostate cancer:
Digital rectal examination
To determine if there are any abnormalities in your prostate, your doctor will examine it through the rectum.
Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) level
PSA is a substance produced by the prostate to liquefy the semen. A higher level than normal may indicate the presence of cancer.
Multiparametric MRI (mpMRI)
Where suspicious tumours can be accurately located.
Transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy or Transperineal MRI fusion biopsy
Once the suspicious tumours are located, they can be sampled either through the rectum using an ultrasound probe on its own or through needles piercing the perineum with targeting aided by the MRI which is more accurate.
Digital rectal examination
One of the most common types of cancer among men is prostate cancer. Various methods can be used to stage prostate cancer to determine the disease’s stage, such as CT, MRI, and bone scintigraphy. Galium-68 PSMA PET CT can be used to image the entire body and detect the spread of diseased tissue with high sensitivity. It has not been possible to observe early metastatic spread to lymph nodes and bones until recently. PSMA PET/CT is a cutting-edge diagnostic technology for locating and determining the extent of prostate cancer utilising galium-68. By using PSMA scans, therapy can be targeted more directly since lymph nodes, bones, and the prostate can be assessed.
To determine whether prostate cancer has spread, your doctor may perform scans of the pelvis and bone.
To successfully treat prostate cancer, a skilled multidisciplinary team must be assembled as numerous treatment options are available. To provide the most advanced treatment options for patients with early or advanced prostate cancer, SJMC brings together the most advanced resources available.
Our team of urologists, clinical oncologists, and radiologists created multidisciplinary treatment plans. Each of our doctors ensures that each patient is fully informed about factors such as the stage and grade of his tumour, the range of treatment options and possible side effects. A physician at this facility can assist patients in navigating the sometimes-complex choices presented by these factors.
Immediate treatment is unnecessary if prostate cancer is not advanced and slow growing. Based on the patient’s cancer characteristics, active surveillance will be recommended, deferring treatment for the time being while on close monitoring.
Also known as radical prostatectomy by surgically removing the prostate and the tissue surrounding it. Usually, a sample of lymph nodes nearby tissue will be removed to ascertain if cancer has spread beyond the prostate.
Combination of hormonal and chemotherapy. Hormonal therapy can also be combined with radiotherapy.
Radiation therapists use high-energy rays from an external beam (like an x-ray) or brachytherapy (implantation of radioactive seeds) to treat prostate cancer.
SJMC's Cancer & Radiosurgery Centre is equipped with the sophisticated and highly advanced Tomotherapy Hi-ART system & Varian TrueBeam system.

There was difficulty in targeting radiation beams precisely in the past, which caused harm to healthy tissues during cancer treatment; today, new systems used at SJMC have brought Radiation Therapy into the 21st century.
Helical tomotherapy combines three-dimensional imaging with innovative intensity-modulated radiation therapy, or IMRT, to primarily target the tumour while sparing nearby healthy tissues.

Using Varian TrueBeam STX technology, also known as RapidArc, Volumetric Arc Therapy (VMAT) delivers fast and accurate radiation treatment.
Lutetium-177 PSMA Therapy, or Prostate-Specific Membrane Antigen Therapy, is an increasingly popular treatment for people with advanced prostate cancer. By using this therapy, the tumour will be reduced in size and will not multiply, as well as the symptoms associated with these tumours will be eased. Usually, it is used when the disease has metastasised, and other therapies have been ineffective or poorly tolerated.
Diet workshops
Support group activities
Yoga & Exercise workshops
SJMC Cancer & Radiosurgery Centre has been recognised for its leadership in cancer management.
The staff members and doctors at the centre are dedicated to providing the best possible care for each patient and aim to enhance the patient's emotional and physical well-being. The facility also offers various support groups and other services to help ease the daily stress of living with cancer.