Leukaemia is a blood cancer. The term leukaemia is derived from a Greek word which literally means white blood. At SJMC’s Cancer and Radiosurgery Centre, we understand that the root cause of leukaemia is the uncontrolled production of abnormal white cells. These abnormal cells fail to mature properly, leading to various complications. Leukaemia is broadly classified into acute leukaemia and chronic leukaemia
In acute leukaemia, the disease progresses quickly, and the leukaemia cells are predominantly immature cells called blasts. Patients become ill within weeks and, if left untreated, will usually succumb to the disease within weeks or months.
ALL
AML
The distinction is based on the fact that they arise from different cells.
There are marked differences in the biology and behaviour of these diseases, their treatment regimens and outcomes; hence the importance in differentiating them from each other.
Using the French-American British (FAB) classification, ALL is further subclassified into L1 to L3, while AML has subtypes Mo to M7. FAB classification is based on the morphological appearance of blasts.
It is useful to classify leukaemia as accurately as possible so that we can gain more understanding of each subtype by comparing results between various centres. The latest classification of acute leukaemia is the MIC (morphologic, immunologic, cytogenetic) classification which integrates morphology with the immunology and karyotype of the leukaemic cells.
Chronic leukaemia, in contrast, has slow disease progression, and both mature and immature cells are seen. Patients may have symptoms for months, and prolonged survival (years) is possible, sometimes even with no treatment. Chronic leukaemia is similarly divided into two types; Chronic Myeloid Leukaemia (CML) and Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL). Again, the distinction is made on the basis of cell origin and individualised management.
In the majority of patients with leukaemia, no predisposing causes can be identified.
It is not inherited except in a few unusual cases, e.g. children with Down's syndrome have an increased risk of getting acute leukaemia. The current concept of leukaemogenesis (how leukaemia arises) is that oncogene and tumour suppressor genes play essential roles, respectively both oncogene and tumour suppressor genes are genes that control cell production and ensure normal synthesis of blood cells.
However, in situations where they are out of control (deregulated) because of damage due to viral infection, chemicals or environmental exposures - the leukaemic process is set in motion. Leukaemia, like any other cancer, is not infectious and cannot be transmitted by any form of contact.
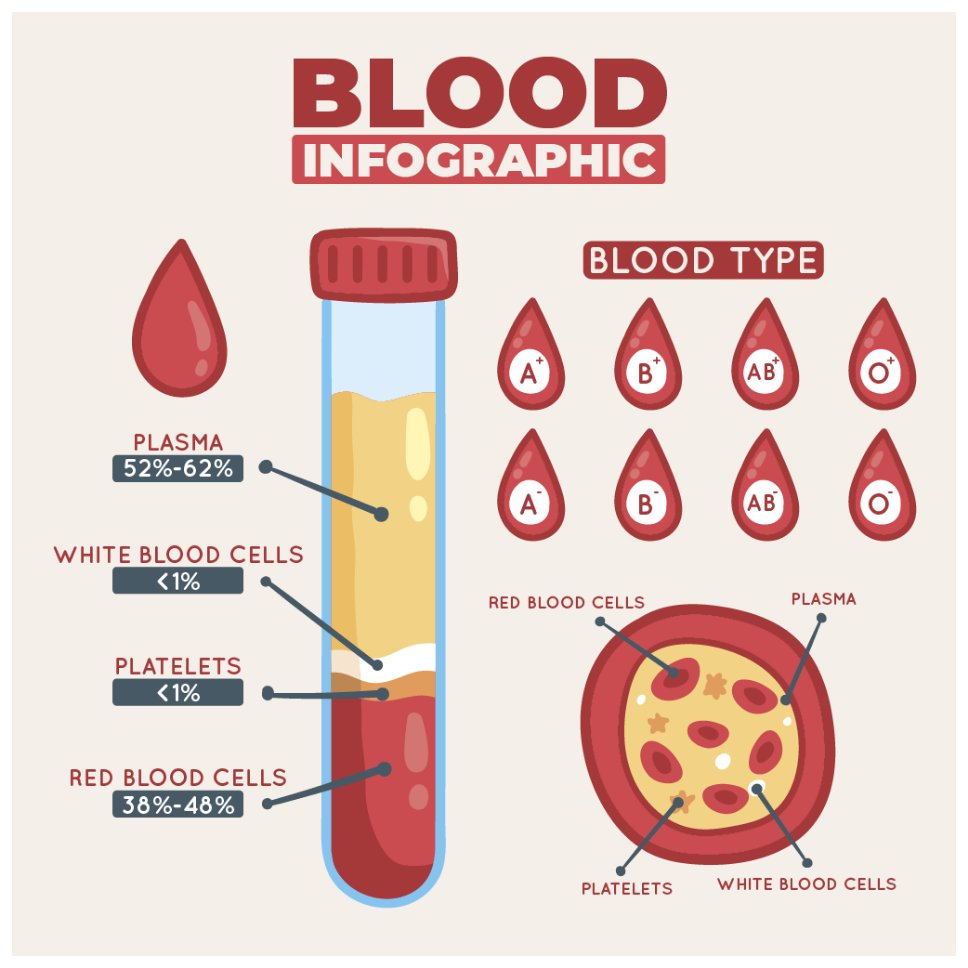
The three main blood cells produced by the bone marrow have specific functions:

Red blood cells
Red blood cells (RBC), which number several million in each drop of blood, are responsible for carrying oxygen to various organs together with nutrients and growth factors. They are the most abundant cells in the blood and give blood its red colour.

Platelets
Platelets are the smallest blood cells, but their function is critical as they rush to areas of damaged blood vessels and form a plug (clot) to stop the bleeding temporarily. Eventually, a stable clot forms at the same site with the incorporation of clotting factors.

White blood cells
White blood cells (WBC) (consisting mainly of neutrophils, lymphocytes and monocytes) are our "front-line soldiers" and defend the body against infection from bacteria, viruses and other organisms.
They may also find that the infections do not seem to resolve, and they have a persistent fever. Due to low platelet count, they suffer from bleeding problems - e.g. easy bruising, bleeding from gums or nose and sometimes severe internal bleeding such as bleeding in the stomach or brain.

the cells affected are very early in cell life; hence, the cells remain immature and do not function well. Patients with acute leukaemia, therefore, are more likely to suffer from anaemia, infections and bleeding.

the disease progression is slow and the cells affected are more mature cells which retain some of their normal functions. As a result, some patients may have no symptoms initially. As the disease progresses, they can have the symptoms described earlier.

The attending doctor would need a sample of blood. A blood cell counter machine is used to measure the blood count consisting of haemoglobin, white cell count and platelet count. If healthy, the blood count falls within a range known as the normal range. Abnormalities in the blood count would alert the doctor that something is amiss. In acute leukaemia, the haemoglobin and the platelet count tend to be low, while the white cell count could be high, normal or even low.
The next step is to examine the stained blood film under the microscope. The presence of abnormal white cells or blasts and abnormal blood count.

This is the procedure where a small sample of bone marrow is obtained from the iliac crest or sternum using a specially designed needle. The bone marrow aspirates are smeared and stained. The marrow slides are then examined by a haematologist or hematopathologist using a microscope, and a formal written report will follow.
The aim of the treatment is to restore the normal synthesis of blood cells (haematopoiesis). At SJMC, our goal is to eliminate the predominant abnormal cells, which are the leukaemic cells or blasts, and allow normal cells to re-populate the marrow. This is achieved through the use of cytotoxic drugs, administered under the close supervision of our experienced specialists.
1ST
STEP
As patients have minimal normal marrow reserve, the induction period is the most dangerous treatment period. This is because they tend to have low blood counts and are prone to life-threatening infections or bleeding even with supportive therapy. Failure to achieve remission despite adequate treatment is a poor prognostic feature, though about 15% of such patients could be salvaged with "early" allogeneic bone marrow transplant.
AFTER A MONTH
About a month after the initiation of induction therapy, a repeat marrow examination is done to assess the response to chemotherapy.
A complete remission (CR) means the return of normal blood count with a normocellular marrow with blast constituting less than 5% of the nucleated cells in the marrow.
ONCE REMISSION IS ACHIEVED,
it is mandatory for patients to have follow-up therapy (post-remission treatment). It has been estimated that 1012 leukaemic cells are present at disease presentation, and after remission has been achieved, there is still 108 leukaemic cells present in the body. Hence, if no post-remission treatment is given, the disease invariably returns. This is an important point that cannot be overemphasised, as occasional patients still opt to stop treatment because they feel 'normal' after attaining CR.
The treatment of acute leukaemia should be started as soon as possible. Sometimes, cytotoxic treatment is withheld for a day or two to ensure any concurrent infection or bleeding are under control. Withholding treatment to wait for a 'better' blood count is unwise as the blood count will not improve unless the underlying problem, i.e. leukaemia, is tackled. Patients with low blood counts would need to be supported with blood products during the treatment period.
Patients are usually admitted for the period of intensive induction chemotherapy. This is to allow close monitoring of patients to treat complications related to the disease, and urgent treatments such as administration of IV antibiotics or blood transfusions are necessary as some patients can deteriorate very quickly. Once remission is achieved, some of the remaining treatments can be done as an outpatient/daycare setting.